Nucleic acid extraction or nucleic acid purification is an essential technique in molecular biology. This technique includes isolation, purification and concentration of nucleic acids including DNA and RNA from different samples.
The basic principles of nucleic acid extraction include breaking the structure of cells (such as cell membrane, nuclear envelope or cell wall) by physical or chemical methods. Finally, the released molecules are purified and concentrated to obtain nucleic acid samples with high concentration. The extracted nucleic acids are good samples for various tests such as PCR, Real Time PCR, gene sequencing and southern blot. It also plays an important role in the diagnosis of viral and bacterial infections. Today, this technique has gained great importance in diagnosing the disease of Covid-19.
Nucleic acids extraction steps:
- Cell disruption/Lysis: In this step, the extraction buffer or heat destroys the structures surrounding the nucleic acids. These structures include cell membrane and nuclear envelope. The extraction buffer usually contains SDS along with enzyme (eg protein kinase K), a chelating agent (EDTA) or Tris buffer.
- Separation and purification: In this step, impurities including lipids and proteins are purified.
- Concentration and precipitation: After initial purification, there may still be some amount of impurities. Therefore, different sedimentation methods such as alcohol sedimentation can be used for further purification of nucleic acids. As a result of this step, nucleic acid molecules with a higher concentration are obtained.
Nucleic acids extraction methods:
There are different methods for extracting nucleic acids. In order to choose the appropriate extraction method, factors such as the purpose of extraction, subsequent analyses, the type of nucleic acids, the organism of origin and the type of sample should be considered.
For example, RNA is an unstable molecule, so fresh samples and RNase-free methods should be used. In RNA extraction, especially in plant samples, the removal of impurities is very important. For this reason, materials such as triazole, chloroform and isopropanol are used to remove lipids, carbohydrates, proteins and DNA.
Solid phase extraction
The best method for extracting nucleic acids in high sample numbers:
Solid-phase extraction (SPE) is an efficient method for extracting nucleic acids. In this method, nucleic acids with high purity and concentration are obtained from small volume samples. The obtained nucleic acids are suitable for various purposes. Various nucleic acid detection and extraction kits are available in the market. Since silica is mostly used as a solid phase in this method, it is also called silica dependent extraction.
Steps of solid phase extraction for nucleic acids:
- Cell lysis: extraction buffer is added to the samples. This buffer destroys the membrane and other cell structures.
- Binding to nucleic acids: In this step, nucleic acids are bound to the solid phase, and other molecules pass through the column and are collected in the centrifuge tube to be thrown away.
- Washing: a washing buffer is used to clean impurities.
- Elution: Using a release buffer (such as a hypoosmotic solution such as water, TE buffer, or Tris buffer), the nucleic acids release from the column and accumulate in a centrifuge tube.
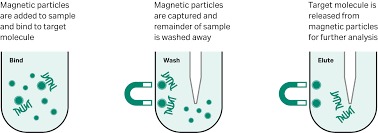
Extraction by magnetic bed method
The magnetic bead method is a modified solid phase method. This method is a reliable way to separate DNA from proteins and other impurities in the sample.
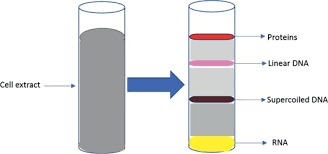
Cesium chloride density gradient extraction
The Cesium Chloride Gradient Centrifugation method is one of the chemical methods for extracting nucleic acids; This method has been the basis of clinical research since the 50s. The basis of this technique is the establishment of nucleic acids in their specific band in the cesium chloride density gradient. In this method, the cesium chloride solution and the cell extract are centrifuged for several hours, and in the resulting density gradient, the molecules are separated based on their specific buoyancy density. Proteins are less dense, and RNA and plasmids with supercoils are more dense than DNA. Finally, ethidium bromide is used to observe the DNA band. Today, this method is used in plasmid extraction. Extracting plasmids from bacterial culture is like the general method of purifying DNA from cells; But in plasmid extraction, it is necessary to separate plasmid DNA from a large amount of bacterial DNA in the cell. For this purpose, there are various methods, one of which is the density gradient of cesium chloride.
Alkaline extraction
Alkaline extraction is a suitable method for plasmid DNA extraction. The alcohol used in this method denatures the chromosomal DNA, but it is covalently linked to the plasmid DNA. After neutralization, chromosomal DNA is precipitated and plasmid DNA remains in the aqueous phase.
Phenol-chloroform extraction
Phenol-Chloroform Extraction, also known as Thiocyanate-Phenol-Chloroform Extraction, is a suitable method for RNA extraction. In this method, after centrifugation, RNA is placed in the blue (upper) phase, and DNA and proteins are placed in the middle and lower phases.
Extraction of CTAB
In this method, a type of detergent called Cethyl trimethyl ammonium Bromide or abbreviated CTAB is used. This method is used to extract plant nucleic acids. Plant samples are rich in various impurities and debris. CTAB forms a complex with nucleic acids and causes their precipitation. While it does not bind to the rest of the substances in the cell extract. The precipitate is washed with salt and nucleic acids are precipitated using alcohol.
Using Chelax particles
This method is used in forensic medicine and criminal investigations. In this method, the traces left at the crime scene, such as blood stains and hair, are sampled. This method helps to preserve the available DNA for PCR despite the small volume of the sample. Chelax are synthetic anionic particles that act as absorbers of polyvalent ions such as magnesium. Removal of these ions causes destruction and inactivation of DNA hydrolyzing enzymes (DNase).
Today, various companies around the world produce and sell automatic nucleic acid extraction devices. These devices have different features and levels of accuracy. China Tianlong Company is a manufacturer of molecular equipment, including automatic nucleic acid extraction devices and their accessories.
These devices can be used in research and medical diagnosis centers. Vesta Tehzih Part Company is the exclusive sales and after-sales service representative of this company. By employing experienced experts, this company has always tried to gain the satisfaction of respected experts and researchers.













